Math5620
Author: David Merkley
Language: Python
Description/Purpose: This code solves a BVP, calculates the error, and calculates a 2-norm of the error. Then it plots all of this information.
Implementation/Code:
import random
import numpy as np
random.seed(10)
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import math
def gridMappingFunc(i, h):
return i * h
def u(x):
return x + 2
def c1(x, y, z):
return 2 / ((y - x)*(y - x + z - x))
def c2(x, y, z):
return 2 / (y - x + z - x)
def c3(x, y, z):
return 2 / ((z - x)*(y - x + z - x))
def main():
xticks = []
xValues = []
A = np.zeros((22, 22))
F = np.zeros(22)
for n in range(22):
xValues.append(random.uniform(n/21, (n+1)/21))
xticks.append(gridMappingFunc(n, 1/21))
for n in range(22):
if n == 0:
F[0] = 2
elif n == 21:
F[n] = 3
else:
F[n] = 0
for n in range(22):
for m in range(22):
if n == 0 and m == 0:
A[0][0] = 1
elif n == 21 and m == n:
A[n][m] = 1
elif n == m:
A[n][m] = c2(xValues[n - 1], xValues[n], xValues[n + 1])
A[n][m - 1] = c1(xValues[n - 1], xValues[n], xValues[n + 1])
A[n][m + 1] = c3(xValues[n - 1], xValues[n], xValues[n + 1])
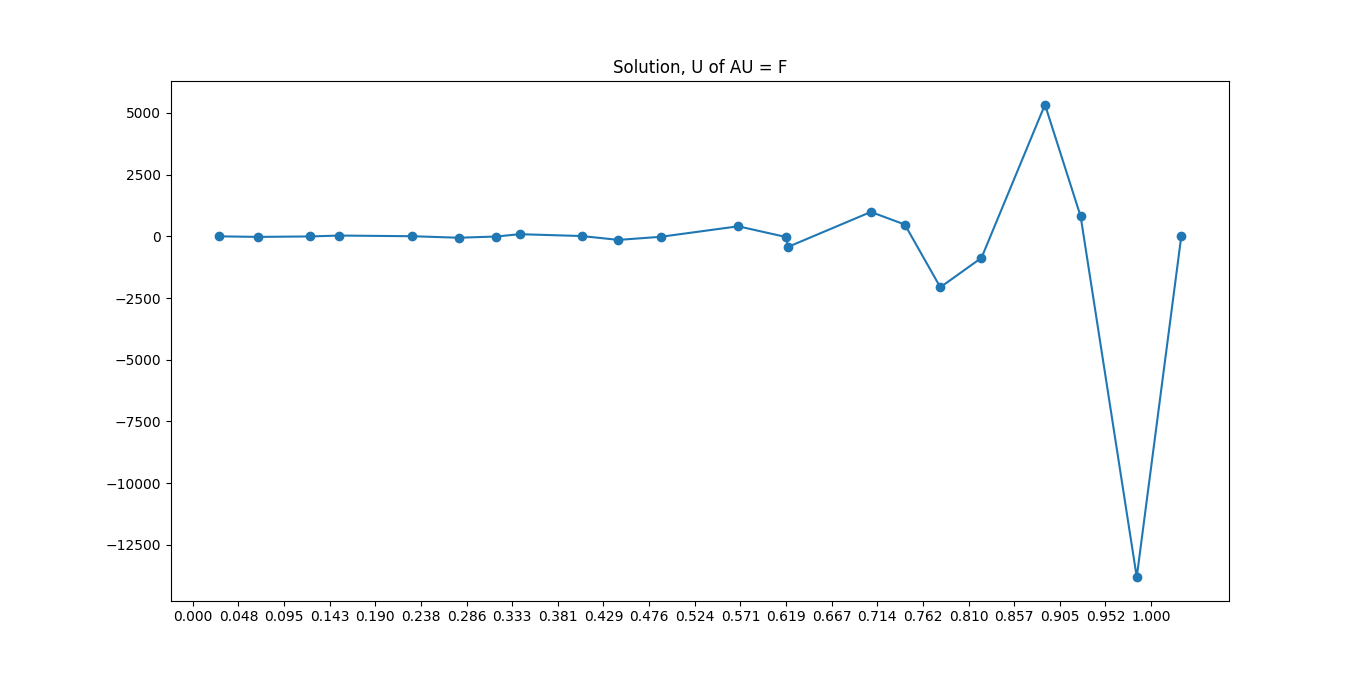
U = np.linalg.solve(A, F)
print("The solution U is:\n", U)
plt.plot(xValues, U, marker='o')
plt.title("Solution, U of AU = F")
plt.xticks(xticks)
plt.yticks()
plt.show()
main()
Output:
The solution U is:
[ 2.00000000e+00 -2.13238104e+01 -2.64276649e+00 3.32003319e+01
5.87242354e+00 -5.48013367e+01 -5.89428622e+00 8.86401865e+01
1.38367204e+01 -1.42655621e+02 -1.78994915e+01 4.08296470e+02
-2.45295709e+01 -4.25797924e+02 9.90161368e+02 4.79413181e+02
-2.06221123e+03 -8.69928735e+02 5.33815831e+03 8.06358191e+02
-1.38065241e+04 3.00000000e+00]